Introduction to Structural Steel Welding
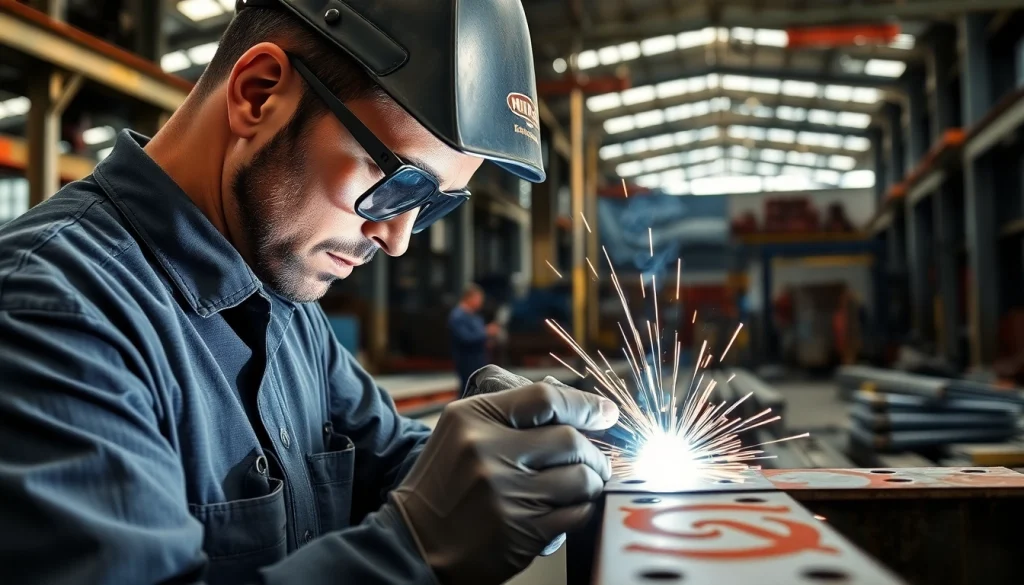
Structural steel welding is a fundamental process in the construction industry, serving as the backbone for durable and robust frameworks. In essence, it involves joining metal components—primarily steel—to produce reliable structures. From bridges to skyscrapers, this technique is pivotal in ensuring safety and stability. The importance of structural steel welding cannot be overstated, as it contributes greatly to both the integrity and longevity of built environments.
What is Structural Steel Welding?
Structural steel welding refers to the method of attaching steel parts together using a welding process. This process can involve various techniques, allowing for different applications based on the project’s requirements. It not only involves the fusion of metals but also requires adherence to safety and quality standards to ensure that the welded structures meet the load-bearing needs and performance specifications.
Importance of Structural Steel Welding in Construction
The role of structural steel welding in construction extends beyond mere connectivity of materials. It supports the entire structural system of buildings, bridges, and other constructions, ensuring they can withstand environmental stresses, such as wind, seismic activity, and loads from various elements. Furthermore, with the growth of urban areas and infrastructural needs, the demand for skilled welders is on the rise, making structural steel welding an essential skill in the trades. The reliability and efficiency of welded joints also lead to faster construction timelines, ultimately benefiting project completion schedules.
Overview of Common Techniques Used
There are several welding techniques utilized in working with structural steel, each catering to different operational and environmental conditions. The common methods include shielded metal arc welding (SMAW), gas metal arc welding (GMAW), and flux-cored arc welding (FCAW). Understanding the unique characteristics and applications of each type is crucial for optimal results, and can help welders select the appropriate method for their specific project needs.
Types of Welding Techniques for Structural Steel
Arc Welding Methods Explained
Arc welding encompasses various techniques that utilize an electrical arc to melt the metal surfaces to be joined. There are several forms of arc welding, with each method having distinct advantages. For instance, SMAW is known for its versatility and is ideal for outdoor sites due to its resistance to wind and moisture. GMAW, also known as MIG welding, provides cleaner welds and is faster compared to SMAW, making it suitable for production work.
MIG vs. TIG Welding for Structural Applications
While both MIG (Metal Inert Gas) and TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding are widely used, they serve different purposes in structural steel welding. MIG welding employs a continuously fed wire and is typically easier for beginners to master. It is faster and ideal for thicker materials, though it may not provide the same level of control as TIG welding. On the other hand, TIG welding offers a high degree of precision and control, making it suitable for thin sections and applications that require superior aesthetics.
Flux-Cored Arc Welding: Advantages and Uses
Flux-cored arc welding (FCAW) is a semi-automatic or automatic welding process that uses a tubular wire filled with flux. A significant advantage of FCAW is its ability to perform well in outdoor conditions and its rate of productivity. It is often used in construction and shipbuilding due to its strong, durable welds and flexibility in various positions (flat, horizontal, vertical, and overhead).
Materials and Equipment for Structural Steel Welding
Essential Types of Steel for Welding
Structural steel is categorized by its specifications which outline its chemical and physical properties. Common types include carbon steel, alloy steel, and stainless steel, each having its advantages in various construction applications. When selecting steel for welding, factors like strength, corrosion resistance, and weldability must be considered to ensure the right fit for the intended use.
Required Tools and Safety Equipment
Safety is paramount in structural steel welding. Essential tools include welding machines, protective gear (helmets, gloves, jackets), and measurement instruments. Proper ventilation and protective barriers are also vital to protect welders from fumes and sparks. Maintenance of tools and adherence to safety protocols not only enhances productivity but also safeguards the health of operators.
Welding Machines: A Buying Guide
When purchasing a welding machine, key considerations should include the welding method it supports, the machine’s output capacity, and the duty cycle. The choice between MIG, TIG, or stick welding machines will depend on the types of projects one intends to undertake. Factors such as portability, ease of use, and cost also play a crucial role in this decision-making process.
Best Practices for Successful Structural Steel Welding
Preparation Steps Before Welding
Good preparation is critical for successful welding outcomes. This involves cleaning the base material to remove rust, grease, and any other contaminants, ensuring clean and stable joint surfaces. Welders should also inspect the materials for defects, establish a clear workspace, and ensure that all necessary equipment is ready and functioning properly.
Techniques to Ensure Strong Welds
To produce strong, reliable welds, welders should utilize correct welding techniques such as maintaining proper arc length, appropriate travel speed, and angle of the torch. Additionally, understanding the thermal dynamics at play is key to preventing issues like warping and distortion during the joint formation. Consistent practice and adherence to standards will enhance the overall quality of welds made.
Post-Weld Inspection and Quality Control
After welding, it’s essential to conduct thorough inspections to verify the integrity of the welds. Techniques like visual examinations, ultrasonic testing, and radiographic testing can help identify flaws or weaknesses. Ensuring compliance with relevant codes and standards, such as the AWS D1.1 for structural welds, is crucial in maintaining the quality of the work.
Future Trends in Structural Steel Welding
Innovations in Welding Technology
The field of structural steel welding is continually evolving, with advancements in technology paving the way for more efficient techniques. Innovations such as robotic welding and automated processes are streamlining operations and improving precision, reducing manual labor requirements while also enhancing safety and productivity.
Sustainability Practices in Steel Welding
As the construction industry increasingly embraces sustainability, eco-friendly welding practices have emerged. This includes reducing waste, recycling materials, and employing energy-efficient welding methods. Companies are now evaluating their carbon footprints and taking steps to enhance their sustainability initiatives, catering to growing environmentally conscious market demands.
Growing Demand for Skilled Welders
The demand for skilled welders continues to rise due to increasing infrastructure projects and emerging technologies. To ensure quality in future construction efforts, educational programs and apprenticeships are being emphasized, leading to a more skilled workforce trained in the latest welding techniques and safe practices. Additionally, with an aging workforce, opportunities for new welders are becoming more abundant.
Frequently Asked Questions
What process is commonly used for structural steel welding?
The most commonly used processes include shielded metal arc welding (SMAW), gas metal arc welding (GMAW), and flux-cored arc welding (FCAW). The choice among these depends on the specific requirements of the project.
What role does a structural steel welder play?
A structural steel welder is essential in construction, responsible for fabricating and installing iron or steel components, such as beams and girders, ensuring structural integrity and safety.
Is structural steel welding a good career choice?
Yes, structural welding offers strong job security due to high demand in construction and infrastructure projects. Skilled welders are sought after, providing ample career opportunities and growth potential.
What distinguishes MIG welding from TIG welding?
MIG welding is generally faster and easier to learn, making it ideal for thicker materials. TIG welding, although more complex, provides superior control and is best for thin sections where precision is critical.
Are there certification programs for structural welders?
Yes, there are various certification programs available that assess a welder’s skills and knowledge in structural steel welding, enhancing their employment prospects and credibility in the industry.