Understanding Structural Steel Installation
What is Structural Steel Installation?
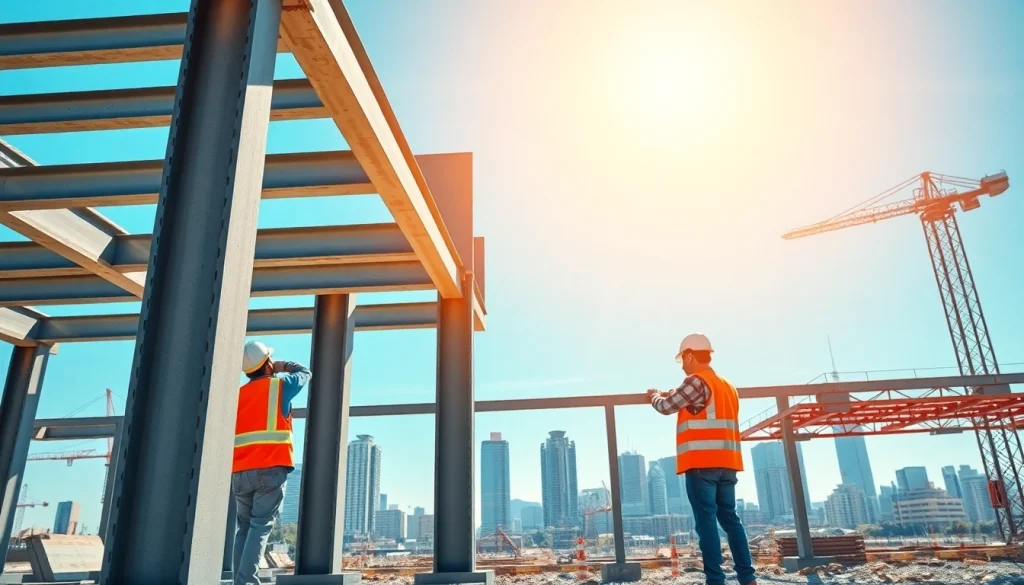
Structural steel installation refers to the process of assembling steel components to create a framework that provides support for structures such as buildings, bridges, and towers. This process involves various stages, from the initial design and planning phase to the physical assembly of steel columns, beams, and deckings on-site. The precise execution of structural steel installation is critical in ensuring the stability of the final structure and its ability to withstand various stresses and loads throughout its lifespan.
Importance of Structural Steel in Modern Construction
In the realm of modern construction, structural steel is favored due to its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, durability, and adaptability. It provides several advantages over traditional materials like wood and concrete:
- Strength: Structural steel can support larger loads compared to other materials, making it ideal for high-rise buildings and expansive structures.
- Speed of Construction: Steel components can be prefabricated off-site, allowing for quicker assembly on-site.
- Durability: Steel is resistant to various environmental factors, which reduces maintenance costs over time.
- Design Flexibility: Steel’s ability to be molded into different shapes opens up a world of architectural possibilities.
Basic Components Involved in Structural Steel Installation
The primary components involved in structural steel installation include:
- Beams: Horizontal structural elements that bear loads from above.
- Columns: Vertical elements that support beams and distribute loads downward.
- Braces: Diagonal elements that provide stability and prevent lateral movement.
- Decking: Horizontal surfaces that create floors and roofs, often made from metal or composite materials.
- Connectors: Various bolts, welds, and fasteners that join steel components together.
Preparation for Structural Steel Installation
Site Assessment and Planning
Proper planning is crucial for a successful structural steel installation. This process begins with a detailed site assessment, which involves examining the land and existing structures. Key factors to consider include soil conditions, proximity to utilities, and environmental concerns. Engineers and architects must collaborate to ensure the design accommodates the site’s unique characteristics.
Necessary Equipment and Tools
The equipment and tools required for structural steel installation vary based on the complexity and scale of the project. Essential tools include:
- Cranes: Used to lift heavy steel components into place.
- Hoists: Essential for positioning and securing materials at height.
- Welding Equipment: Necessary for connecting steel components permanently.
- Safety Gear: Personal protective equipment (PPE) including helmets, gloves, and harnesses to ensure worker safety.
Safety Considerations Before Installation
Safety is paramount during structural steel installation. Project managers must establish a comprehensive safety plan that includes:
- Conducting safety training for all workers.
- Performing regular equipment inspections and maintenance.
- Implementing first aid measures and emergency procedures.
- Ensuring proper use of PPE at all times.
- Setting clear communication protocols for all team members.
Steps in the Structural Steel Installation Process
Initial Setup and Foundation Work
Effective structural steel installation begins with a solid foundation. This stage includes excavation, soil compaction, and the placement of concrete footings. The foundation must be designed to bear the intended loads of the structure, and it often requires the expertise of civil and structural engineers to ensure it meets all building codes and standards.
Beam and Column Assembly Techniques
Once the foundation is ready, the assembly of beams and columns can commence. This process typically follows a systematic procedure:
- Positioning columns: Columns are set in place according to the structural plans, often using cranes.
- Installing beams: Beams are lowered and positioned across the columns, secured using bolts or welds.
- Bracing the structure: Once beams are in position, bracing methods are applied to stabilize the frame.
Final Calibration and Inspection Procedures
A critical phase in structural steel installation involves calibrating and inspecting the framework. This includes ensuring that all elements are level, square, and properly aligned. Inspectors will use various tools to check for deviations and ensure compliance with design specifications. Any discrepancies must be resolved before moving forward to avoid long-term structural issues.
Best Practices for Successful Structural Steel Installation
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Despite careful planning, challenges often arise during structural steel installation. Common issues include:
- Supply Chain Delays: Steel shortages or delays in delivery can hold up projects. It’s essential to maintain strong relationships with suppliers and have contingency plans in place.
- Weather Conditions: Rain, snow, or extreme temperatures can impede work. Monitoring the weather forecast and planning accordingly is necessary to minimize downtime.
- Safety Incidents: The risk of accidents can never be eliminated entirely. Continuous training and review of safety protocols are crucial for preventing injuries.
Ensuring Quality and Compliance
Quality assurance is vital in every stage of the structural steel installation process. Regular inspections should be conducted to confirm that materials comply with industry standards and specifications. Documentation of inspections and certifications must be maintained to ensure traceability. Furthermore, adherence to local building codes and regulations is essential to avoid legal and safety repercussions.
Training and Team Coordination Tips
Effective communication and collaboration among the installation team can significantly enhance performance and safety. Here are some essential strategies:
- Regular Meetings: Scheduled meetings to discuss project progress and potential issues keep everyone informed and engaged.
- Clear Roles and Responsibilities: Each team member should know their specific roles to minimize confusion and streamline operations.
- Encouraging Feedback: Team members should feel comfortable bringing forward concerns or suggestions to facilitate improvement.
Evaluating the Success of Structural Steel Installation
Key Performance Metrics to Monitor
To gauge the success of structural steel installation, several performance metrics should be outlined and monitored:
- On-Time Completion: Measure whether the project met its deadlines.
- Budget Adherence: Track costs throughout the installation process against the projected budget.
- Safety Incidents: Record any accidents or near misses and analyze this data to improve safety protocols.
- Quality of Work: Post-installation evaluations help identify any deficiencies that may require rectification.
Post-Installation Inspection Checklist
After completing the installation, a thorough inspection checklist ensures that all components meet specified standards. This includes:
- Verification of structural integrity through load tests.
- Visual inspections for welds and bolt connections.
- Assessing bracing and anchoring systems.
- Reviewing documentation for compliance with design specifications.
Case Studies of Successful Projects
Examining successful case studies can provide insights into effective practices during structural steel installations. Common themes in such cases include strong team coordination, meticulous planning, and proactive problem-solving. Each project offers a unique learning opportunity that practitioners can draw upon to enhance their approaches in future installations.